Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 7th Edition by Nelson ISBN: 9781464126116 Latest Update PDF Download 2025/2026
Course:
Biochemistry
Institution:
Biochemistry
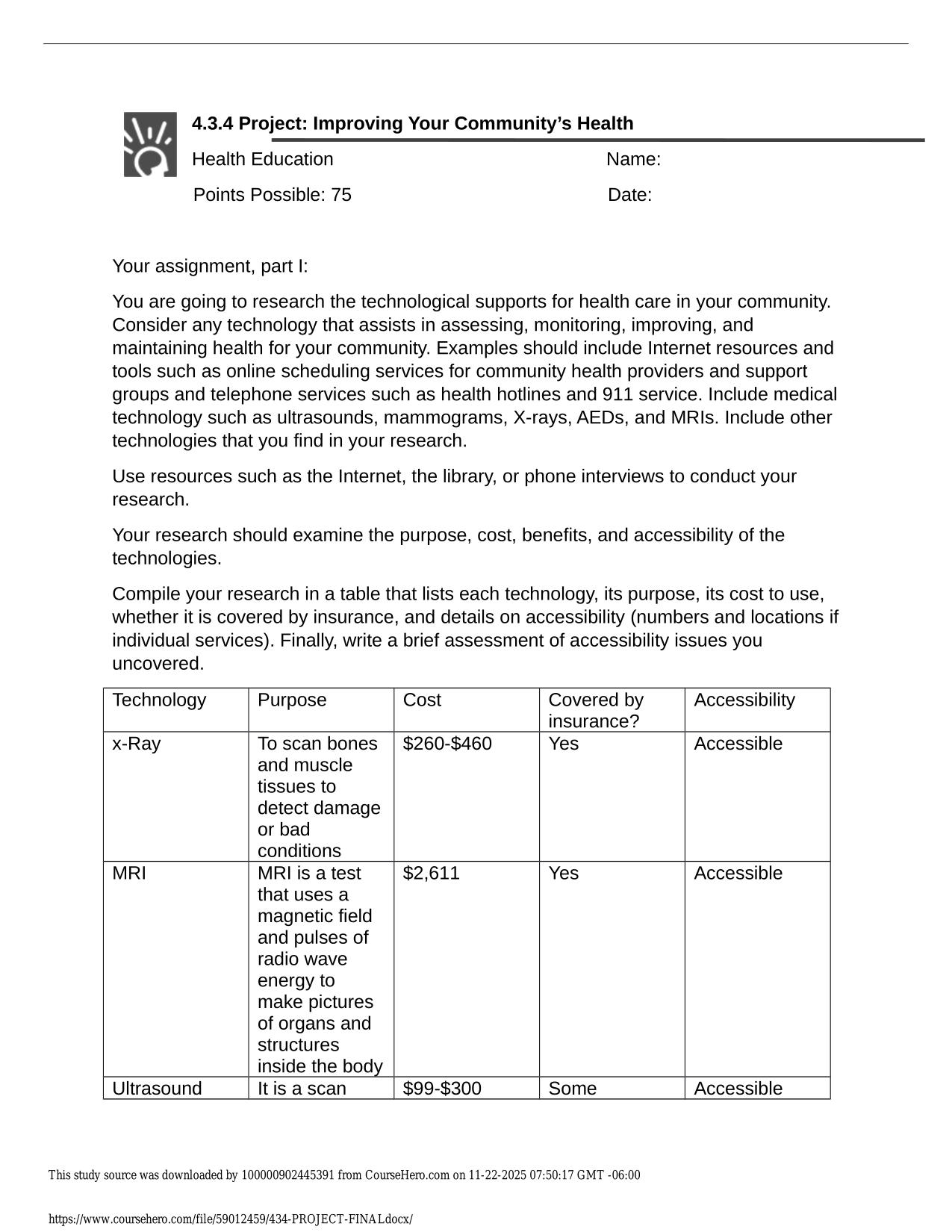
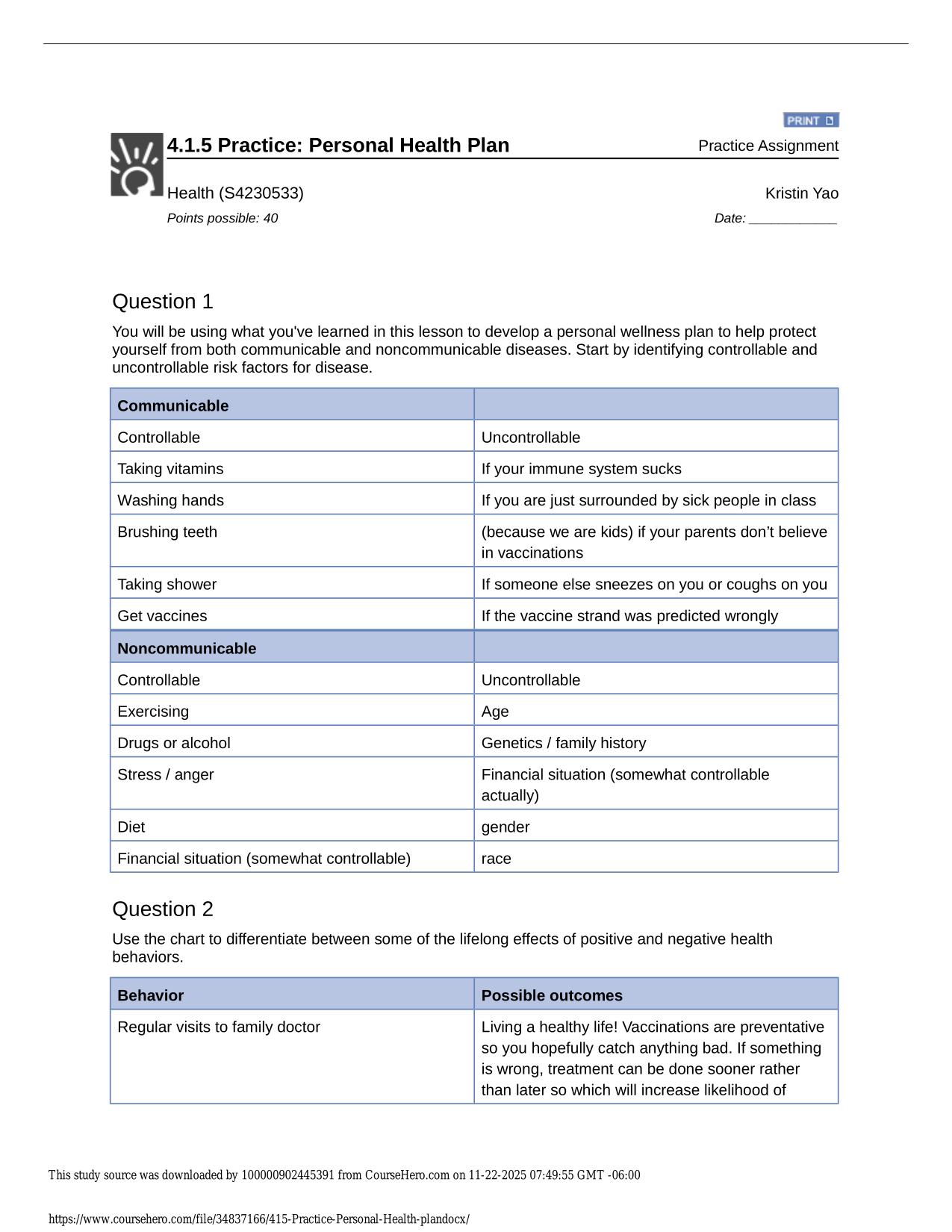
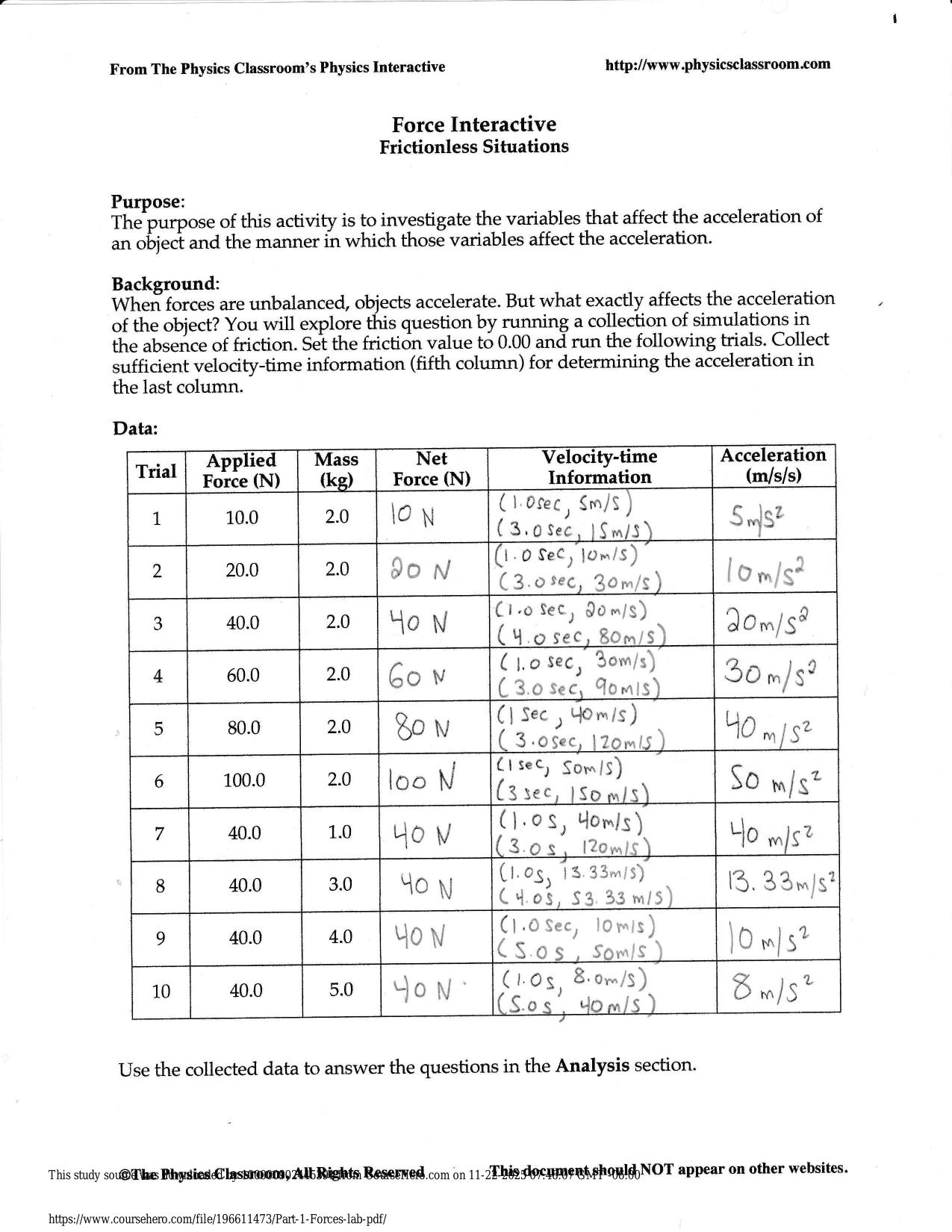
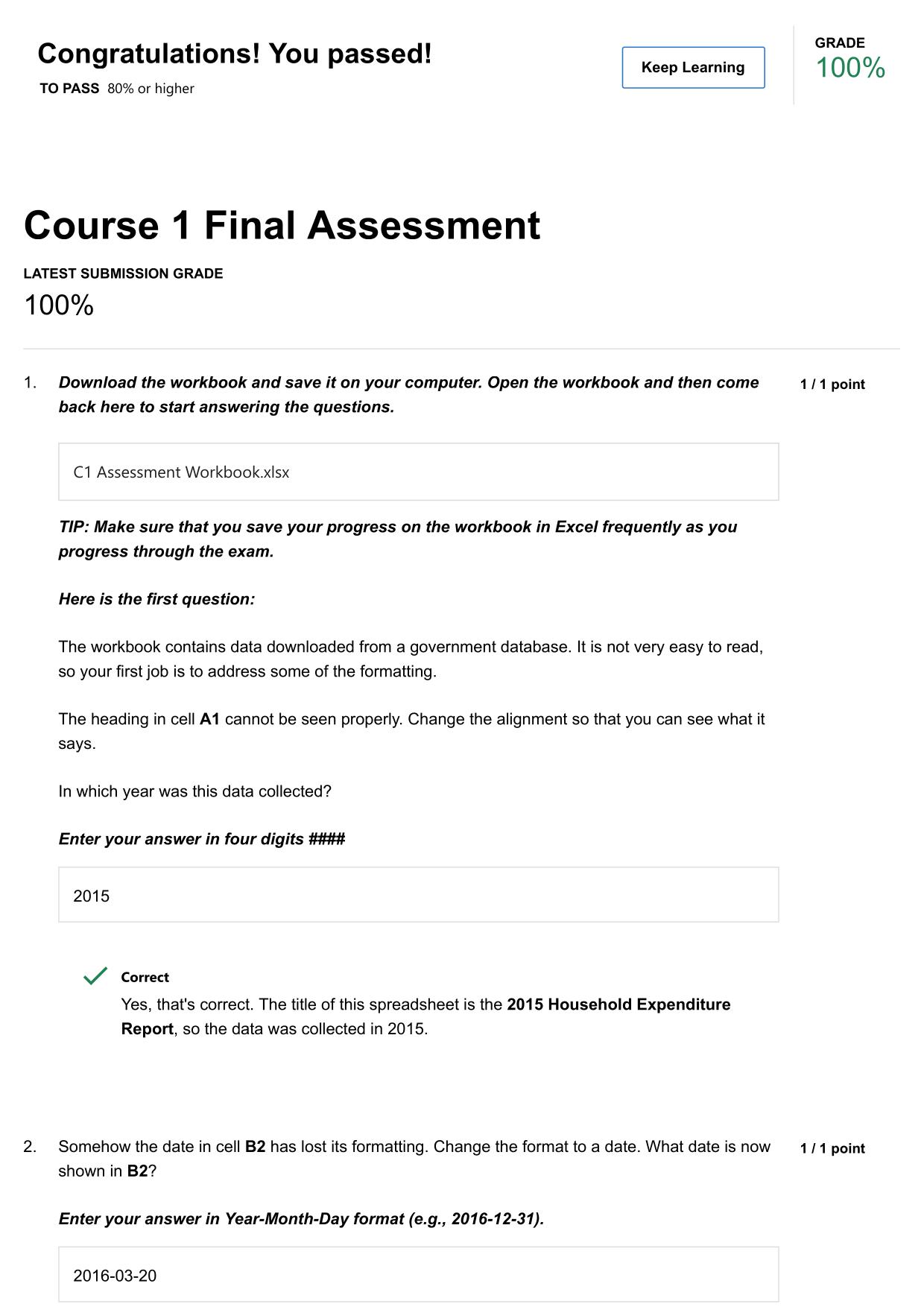
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 7th Edition by Nelson ISBN: 9781464126116 Latest Update PDF Download 2025/2026 1. In a bacterial cell, the DNA is in the: A) cell envelope. B) cell membrane. C) nucleoid. D) nucleus. E) ribosomes. 2....
After purchase, you get:
✅ Instant PDF Download
✅ Verified answer explanations
✅ Refund if not Satisfied
✅ Prepared for 2025/2026 test cycle
Overview
Detailed answer keys help users track progress, address weak spots, and practice under timed conditions. The immediate feedback lets you catch misunderstandings before they become bad habits that are hard to break. Students frequently use these keys to map out their study priorities based on actual performance rather than guesswork. Being able to see exactly where you need improvement turns random studying into a strategic, focused effort that delivers real results. Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 7th Edition by Nelson ISBN: 9781464126116 Latest Update PDF Download 2025/2026 is organized to help learners build assurance with realistic question formats and trusted solutions. Many students find that working through these materials makes the actual exam feel familiar rather than intimidating. The carefully crafted questions help identify areas where you need more practice before test day. You'll notice your anxiety decreasing as you become more comfortable with the testing format through repeated practice.
Who Is This For?
Ideal for students, instructors and professionals preparing for Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 7th Edition by Nelson ISBN: 9781464126116 Update PDF Download / and related Biochemistry exams. Many learners find this format helps them identify knowledge gaps quickly. The material works well for both individual study and classroom settings.
Related Keywords
Detailed Study Description
Frequently Asked Questions
Document Information
| Uploaded on: | November 1, 2025 |
| Last updated: | November 17, 2025 |
| Number of pages: | 478 |
| Written in: | 2025/2026 |
| Type: | Exam (elaborations) |
| Contains: | Questions & Answers |
| Tags: | Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 7th Edition by Nelson ISBN: 9781464126116 Latest Update PDF Download 2025/2026 1. In a bacterial cell, the DNA is in the: A) cell envelope. B) cell membrane. C) nucleoid. D) nucleus. E) ribosomes. 2. A major change occurring in the evolution of eukaryotes from prokaryotes was the development of: A) DNA. B) photosynthetic capability. C) plasma membranes. D) ribosomes. E) the nucleus. 3. In eukaryotes, the nucleus is enclosed by a double membrane called the: A) cell membrane. B) nuclear envelope. C) nucleolus. D) nucleoplasm. E) nucleosome. 4. The dimensions of living cells are limited, on the lower end by the minimum number of biomolecules necessary for function, and on the upper end by the rate of diffusion of solutes such as oxygen. Except for highly elongated cells, they usually have lengths and diameters in the range of: A) 0.1 m to 10 m. B) 0.3 m to 30 m. C) 0.3 m to 100 m. D) 1 m to 100 m. E) 1 m to 300 m. 5. Which group of single-celled microorganisms has many members found growing in extreme environments? A) bacteria B) archaea C) eukaryotes D) heterotrophs E) |
Seller Information

AdelineJean
User Reviews (0)
Exam (Elaborations)
$17.00
Add to Cart
100% satisfaction guarantee
Refund Upon dissatisfaction
Immediately available after purchase
Available in Both online and PDF
$17.00
| 0 sold
Discover More resources
Inside The Document
1. In a bacterial cell, the DNA is in the: A) cell envelope. B) cell membrane. C) nucleoid. D) nucleus. E) ribosomes. 2. A major change occurring in the evolution of eukaryotes from prokaryotes was the development of: A) DNA. B) photosynthetic capability. C) plasma membranes. D) ribosomes. E) the nucleus. 3. In eukaryotes, the nucleus is enclosed by a double membrane called the: A) cell membrane. B) nuclear envelope. C) nucleolus. D) nucleoplasm. E) nucleosome. 4. The dimensions of living cells are limited, on the lower end by the minimum number of biomolecules necessary for function, and on the upper end by the rate of diffusion of solutes such as oxygen. Except for highly elongated cells, they usually have lengths and diameters in the range of: A) 0.1 m to 10 m. B) 0.3 m to 30 m. C) 0.3 m to 100 m. D) 1 m to 100 m. E) 1 m to 300 m. 5. Which group of single-celled microorganisms has many members found growing in extreme environments? A) bacteria B) archaea C) eukaryotes D) heterotrophs E) None of the answers is correct. Page 1 6. The bacterium E. coli requires simple organic molecules for growth and energyóit is therefore a: A) chemoautotroph. B) chemoheterotroph. C) lithotroph. D) photoautotroph. E) photoheterotroph. 7. Which is a list of organelles? A) mitochondria, chromatin, endoplasmic reticulum B) peroxisomes, lysosomes, plasma membrane C) proteasomes, peroxisomes, lysosomes D) mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisomes E) All of the answers are correct. 8. Which list has the cellular components arranged in order of INCREASING size? A) amino acid < protein < mitochondrion < ribosome B) amino acid < protein < ribosome < mitochondrion C) amino acid < ribosome < protein < mitochondrion D) protein < amino acid < mitochondrion < ribosome E) protein < ribosome < mitochondrion < amino acid 9. The three-dimensional structure of macromolecules is formed and maintained primarily through noncovalent interactions. Which one of the following is NOT considered a noncovalent interaction? A) carbon-carbon bonds B) hydrogen bonds C) hydrophobic interactions D) ionic interactions E) van der Waals interactions 10. Which element is NOT among the four most abundant in living organisms? A) carbon B) hydrogen C) nitrogen D) oxygen E) phosphorus Page 2 11. The four covalent bonds in methane (CH4) are arranged around carbon to give which geometry? A) linear B) tetrahedral C) trigonal bipyramidal D) trigonal planar E) trigonal pyramidal 12. What functional groups are present on this molecule? A) B) C) D) E) ether and aldehyde hydroxyl and aldehyde hydroxyl and carboxylic acid hydroxyl and ester hydroxyl and ketone 13. The macromolecules that serve in the storage and transmission of genetic information are: A) carbohydrates. B) lipids. C) membranes. D) nucleic acids. E) proteins. 14. Stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other are known as: A) anomers. B) cis-trans isomers. C) diastereoisomers. D) enantiomers. E) geometric isomers. Page 3
CourseHero & Studypool Unlocks
Get Unlocked CourseHero and Studypool documents files instantly to your email, simply by pasting your link and clicking "Unlock Now". Learn more on how to unlock here.